The core difference isn’t about the light itself, but about how they manage the single biggest enemy of LEDs: Heat.
Here’s a breakdown of fanless vs. fan LED headlights.
The Core Problem: Why LED Headlights Need Cooling
Despite being highly efficient, LED chips still generate a significant amount of heat, concentrated at a tiny semiconductor junction at their base.
-
The Danger Zone: If this junction temperature gets too high (typically above 150°C / 302°F), the LED will:
-
Lose Brightness (Lumen Depreciation): It will permanently and rapidly dim over its short lifespan.
-
Shift Color: The white light can become bluer or change hue.
-
Fail Prematurely: The LED chip or its internal components can be destroyed, leading to a dead headlight.
-
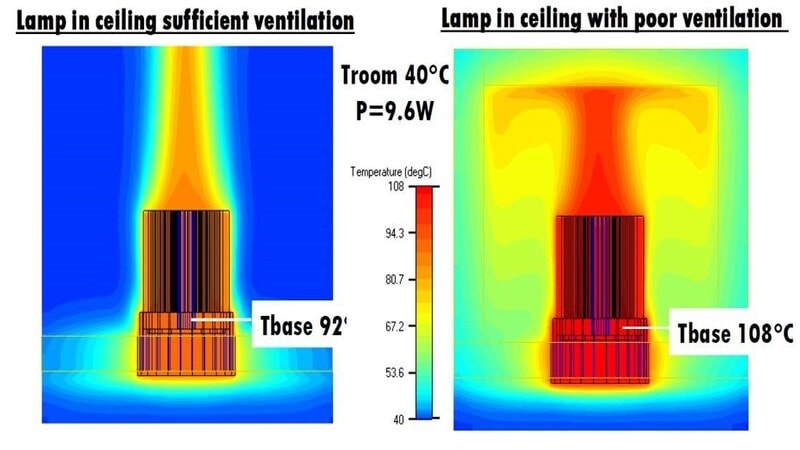
The goal of any cooling system is to pull this heat away from the LED chip and dissipate it into the surrounding air as quickly as possible.
Fan-Cooled (Active) LED Headlights
This is the most common type, especially for aftermarket LED replacement bulbs.
How It Works:
A small but powerful fan is attached to the base of the headlight. The fan actively pulls air across a set of fins (a heatsink) that are in direct contact with the LED board, forcing hot air away.

Pros:
-
High Cooling Efficiency: Fans can move a lot of heat in a compact space, making them highly effective for high-power LEDs.
-
Compact Design: Allows for a smaller overall heatsink, which is crucial for fitting into the confined spaces of a vehicle’s headlight housing.
-
Effective in Stagnant Air: They work well even when there’s no airflow from the vehicle’s movement.
Cons:
-
Moving Parts = Potential Failure: The fan is a mechanical component with bearings that can wear out, collect dust/debris, and eventually fail. A dead fan means rapid LED overheating and failure.
-
Noise: Some fans produce a faint but audible high-pitched whirring or buzzing sound.
-
Dust and Moisture: The fan can potentially draw moisture, condensation, or dust into the assembly if not properly sealed.
Best For:
-
Aftermarket LED bulbs that need a powerful cooling solution in a small form factor to fit inside existing halogen headlight housings.
-
High-output performance headlights.
Fanless (Passive) LED Headlights
This method relies solely on physics without any moving parts. It’s often found in higher-end, custom, or OEM (original equipment manufacturer) LED headlight assemblies.
How It Works:
These systems use a large, often elaborate, heatsink made of conductive metal (like aluminum). The heat from the LED travels through the metal fins, and the large surface area of the fins then passively radiates the heat into the surrounding air. Some advanced designs may use heat pipes—sealed tubes containing a fluid that vaporizes at the hot end, carries the heat to the cool end (the fins), condenses, and cycles back—to move heat even more efficiently.


Pros:
-
Extreme Reliability: No moving parts to break. This is the single biggest advantage. The lifespan is typically limited only by the LED itself.
-
Silent Operation: Zero noise.
-
Dust/Moisture Resistant: With no fan to draw things in, they are generally better sealed against the elements.
Cons:
-
Large Physical Size: To be as effective as a fan-cooled system, a passive heatsink needs to be significantly larger to have enough surface area.
-
Dependent on Airflow: Their efficiency can be slightly reduced if mounted in a completely stagnant, enclosed space. They often rely on some ambient airflow from the vehicle’s movement.
-
Weight and Cost: The large amount of metal and complex engineering (like heat pipes) can make them heavier and more expensive to manufacture.
Best For:
-
OEM LED Headlights from car manufacturers, where the entire headlight assembly is designed from the ground up to accommodate the large heatsink.
-
High-quality, reliability-focused aftermarket headlights or off-road light bars that have the space for a large heatsink.
Comparison Table: Fanless vs. Fan-Cooled

| Feature | Fan-Cooled (Active) | Fanless (Passive) |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Fan forces air over a heatsink | Large heatsink radiates heat naturally |
| Reliability | Lower (moving parts can fail) | Higher (no moving parts) |
| Noise | Can produce a faint whirring | Completely silent |
| Size/Form Factor | More compact | Larger and bulkier |
| Durability | Good, but vulnerable to fan failure | Excellent |
| Cost | Generally less expensive | Often more expensive |
| Common Use | Aftermarket LED replacement bulbs | OEM LED assemblies, premium lights |
Which One Should You Choose?
-
For replacing halogen bulbs in your existing car: You will almost certainly be looking at fan-cooled LED bulbs. Their compact design is necessary to fit inside the dust cap of your headlight housing. When buying, choose reputable brands known for using quality, long-life fans.
-
For a new vehicle or a full headlight assembly replacement: If the vehicle comes with OEM LEDs or you’re buying a complete aftermarket LED assembly, it likely uses a fanless design. This is a sign of a well-engineered, durable system designed to last the life of the vehicle.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Which type is more reliable, fanless or fan-cooled?
A: Fanless systems are generally more reliable in the long term because they have no moving parts. A fan is a mechanical component that will eventually wear out, while a well-made heatsink can last virtually forever.
Q2: I hear a faint buzzing from my new LED headlights. Is this normal?
A: For fan-cooled bulbs, a faint high-pitched whirring from the fan is normal. However, a loud buzzing or clicking sound is not and could indicate a faulty fan or an electrical issue with the bulb’s driver.
Q3: Can I use a fan-cooled LED bulb in a sealed headlight housing?
A: It’s not recommended. While the fan will move heat, a completely sealed housing traps all the hot air, creating an oven-like environment that can overwhelm any cooling system and lead to premature failure. Proper ventilation is key.
Q4: My fan-cooled LED bulb stopped working. Could the fan be the cause?
A: Absolutely. If the fan fails, the LED chip will overheat very quickly, often in a matter of minutes, leading to irreversible damage. This is one of the most common failure points for fan-cooled LEDs.
Q5: Are fanless bulbs always better?
A: Not always. While more reliable, their large size often makes them incompatible with simply replacing a halogen bulb in your existing headlight housing. They are best when the entire headlight assembly is designed for them from the start.
Conclusion
The choice isn’t about one being universally “better” than the other. It’s about the application. Fan-cooled offers power and size efficiency, while fanless offers ultimate reliability and silence. Both are excellent solutions to the critical problem of LED thermal management when implemented correctly.

Source Your Ideal Headlight Now!
The LED experts at Car Light Wholesale are waiting to help you make a smart LED light purchase decision today. Whether you want Fan-cooled or fanless LED headlights, trust us for bulk purchases of lights that will last.
Contact us today for bulk orders and wholesale purchase of LED headlights of all kinds. Get your hands on the best headlights with expert advice and service that you’d remember forever!






